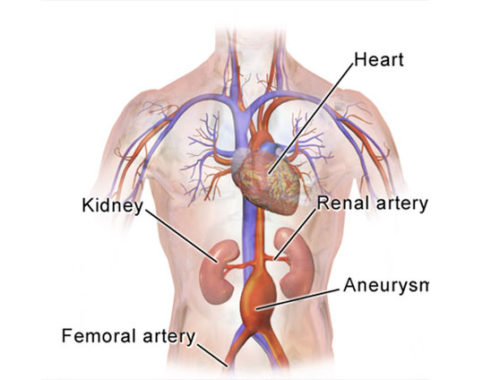
The “abdominal aorta” is the part of the aorta that goes from the heart down through the belly, and then branches to supply blood to the legs. An “abdominal aortic aneurysm,” also known as an “AAA,” occurs when a part of the wall of the abdominal aorta becomes weak and balloons out or bulges. If the aneurysm bursts, the condition becomes very dangerous, causing serious bleeding and in many cases lead to death.
What are the symptoms of an AAA?
Most people with abdominal aortic aneurysms have no symptoms and the aneurysms can burst with no warning. Doctors suggest you get tested if there is a high risk that you might have AAA. When symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Pain in the belly or back
- A small lump in the upper part of the belly that pulses with the heartbeat
Who is at risk for AAA?
- Men, especially those older than 60 (with every year of life after that, your risk goes up even more)
- Smokers
- People with a family history of AAA
- People who have heart disease or other conditions that affect the blood vessels
Can AAAs be prevented?
No. But you can greatly reduce your risk by not smoking and controlling your blood pressure.
How do I test for AAA?
The simplest test is an ultrasound of the aorta. Other tests include CT scan or MRI of the abdomen. These aneurysms are sometimes associated with aneurysms in other parts of the body.
When are AAAs treated?
That depends on how big the aneurysm is. The bigger the aneurysm, the greater the risk of rupture and bleeding. Most people with AAA measuring over 5 cm need treatment. People with aneurysm measuring over 4cm need close monitoring. Aneurysms that grow more than 0.5cm in 6 months often need to be treated.
How are AAAs repaired?
Aneurysms can be fixed in one of two ways:
- Traditional “open” surgery – For open surgery, the doctor cuts open your belly and replaces the bulging part of the aorta with a tube called a “graft” so that blood can flow normally through it.
- Endovascular stent graft – This is a less-invasive procedure to deliver a stent with folded graft material that is delivered via a catheter or small tubes through the leg arteries.